Technical information
Step Preventive Pavement HRB
Category :
-
Paving Methods > Roadway > Subsidence Measures >
Prevents pavements from collapsing in an earthquake
Overview
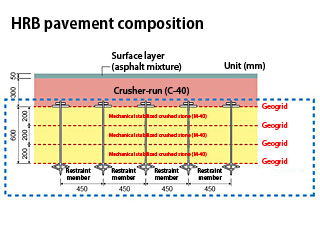
This construction method involves building a composite rigid layer on the subgrade using a high-strength geo-grid and restraining members. It prevents the pavement from collapsing due to an earthquake and inhibits the formation of cracks and bumps in the asphalt pavement road surface. This allows emergency vehicles to travel on the road immediately after an earthquake, thereby helping to accelerate the initial response to any urgent call to save lives and transport supplies.
Features
- By smoothly tracking ground deformations caused by earthquakes while maintaining support performance, cracks and bumps emerging in the asphalt pavement road surface can be inhibited, thereby providing passage to vehicular traffic.
- It is easy to lay down a geo-grid and restraining members. As the composite rigid layer is simply built atop the subgrade, construction work can be carried out in a short period of time within blocked-off lanes without having to set up temporary yards for the storage of large equipment.
Uses
- Large-scale earthquake measures applicable to asphalt pavements
- Preventing the unequal settlement of soft-ground embankment areas and embankment boundaries
- Front and rear of structures
- Sinking around buried structures
- Bump inhibition